The Exploitative System that Traps Nigerian Women as Slaves in Lebanon
Human Rights
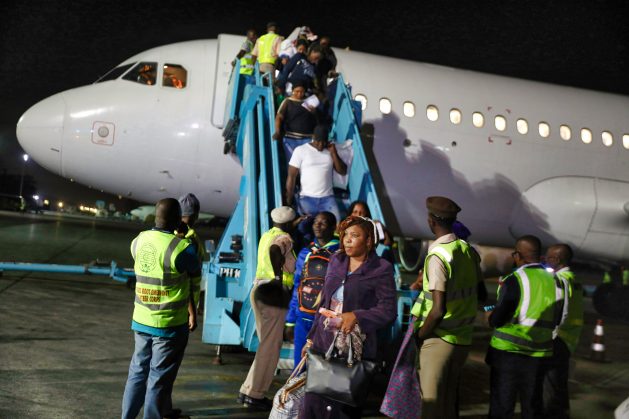
Nigerian migrants arrive in Lagos from Libya. Nigeria has, in the last two years, evacuated thousands of its citizens from Libya and Lebanon after they suffered several forms of abuses, including enslavement. Trafficking has resulted in at least 80,000 Nigerian women being held as sex slaves and forced labour in the Middle East. Credit: Sam Olukoya/IPS
LAGOS, Nigeria, Sep 14 2020 (IPS) - “I need help, right now I cannot walk properly,” trafficking victim Nkiru Obasi pleaded from her hospital bed in a video she posted online.
The young Nigerian woman had been injured in the Aug. 4 Beirut blast, which ripped through the Lebanese capital, killing 190 people injuring a further 6,500 and damaging 40 percent of the city. However, it’s not her injuries keeping her in Lebanon but a restrictive and abusive system of migrant laws.
Obasi is just one of thousands of young Nigerian women trafficked to Lebanon with false promises of a better life. The Lagos-based New Telegraph newspaper quoted a source in the Nigerian embassy in Lebanon as saying that some 4,541 Nigerian women were trafficked to the country last year. The chair of Nigerians in Diaspora Commission, Abike Dabiri-Erewa, described the rate at which Nigerian women are trafficked to Lebanon as “an epidemic”.
After sustaining injuries in the blast, Obasi tried to return to Nigeria but she and four others were stopped at the airport under the exploitative Kafala system.
The system, which is widely practiced in Lebanon and other parts of the Middle East, prohibits migrant workers from returning to their countries without the permission of their employer.
“Lebanon’s restrictive and exploitative kafala system traps tens of thousands of migrant domestic workers in potentially harmful situations by tying their legal status to their employer, enabling highly abusive conditions amounting at worst to modern-day slavery,” according to Aya Majzoub, Lebanon researcher at Human Rights Watch. The rights organisation called for a revised contract that recognises and protects workers’ internationally guaranteed rights.
In late May, Nigeria attempted to repatriate 60 trafficked women from Lebanon but only 50 could return home. Anti-trafficking activists in the Middle East said the remaining 10 women were held back in Lebanon under the Kafala system.
The Kafala system operates alongside a system that enslaves trafficked women. In April, a Lebanese man posted an advert under the “Buy and Sell in Lebanon” Facebook group. “Domestic worker from Nigeria for sale with new legal document, she is 30 years old, she is very active and very clean,” the advert said in Arabic. The price tag was $1,000.
An outcry from Nigeria forced Lebanese authorities to rescue the woman while a man thought to be responsible for the Facebook post was arrested. The Lebanese Ministry of Labour said the man would be tried in court for human trafficking.
But this is not an isolated case. Many Nigerian women trafficked to the Middle East have spoken out about being sold as slaves.
In January, 23-year-old Ajayi Omolola appeared in an online video saying she and a few other Nigerian women were being held under harsh conditions and that their lives were at risk.
“When we are ill, they don’t take us to the hospital, some of those I arrived in Lebanon with have died,” she said.
Omolola said on arrival in Lebanon, her passport was taken away and she was “sold”.
“I did not realise that they had sold me into slavery,” she said, adding that she only realised the gravity of her situation when her boss told her she could not return to Nigeria because he had “bought her”.
Kikelomo Olayide had a similar account. On arrival in Lebanon from Nigeria she was taken to a market. “In that market, they call us slaves,” she said.
Roland Nwoha, head of programmes/coordinator of migration and human trafficking at Idia Renaissance, a Nigerian organisation working to discourage irregular migration and human trafficking, told IPS that even though Europe is a major attraction for Nigerians in search of a better future abroad, the Middle East is proving an alternative for many.
Nwoha explained that unlike the journey to Europe, which involves a dangerous land journey through the desert and an equally dangerous crossing of the Mediterranean Sea, traffickers fly their victims to the Middle East after procuring visas for them with the promise of good jobs.
The chair of Nigeria’s House of Representatives Committee on Diaspora Affairs Tolulope Akande-Sadipe said 80,000 Nigerian women are being held as sex slaves,and forced labour in the Middle East, especially in Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates and Oman.
Nigerian women trafficked to the Middle East “almost always end in labour and sexual exploitation,” Daniel Atokolo Lagos commander of the National Agency for the Prohibition of Trafficking in Persons said.
Gloria Bright, a Nigerian teacher who was promised a teaching job with a monthly salary of $1,000 in Lebanon, was held captive and made to work as a domestic worker upon her arrival. She posted an online video in which she pleaded for help and to be rescued. She said besides being made to work under very harsh conditions, her boss sexually harassed her. “At times he will ask me to massage him, he will hug me, he will kiss me,” she said.
Bright was fortunate to be rescued by Nigerian authorities before the Aug. 4 Beirut blast.
Dabiri-Erewa said the trafficking of Nigerians to Lebanon “is becoming a big embarrassment and it has to be stopped”. In an effort to stop the crime, Nigerian authorities have arrested several people, including Lebanese residents in Nigeria. A Lebanese is being investigated in connection with the trafficking of 27 women to Lebanon, two of whom have been rescued.
The Lebanese ambassador to Nigeria, Houssam Diab, says his embassy is assisting the Nigerian government to stop the trafficking of women to his country. He said the issuance of work visas to Nigerians has been suspended following cases of the abuse of Nigerian women at the hands of their Lebanese employers.
The ambassador said the Lebanese Ministry of Labour will work out a “legal and systemic way to make domestic staff to come into Lebanon legally without the fear of inhuman treatment”.
Nigerian activists, like Nwoha, who are working against human trafficking say the Nigerian government has to do more to curtailing the activities of the traffickers. They said the government should make conditions at home better to stop Nigerians desperately seeking a better life abroad.
This is part of a series of features from across the globe on human trafficking. IPS coverage is supported by the Airways Aviation Group.
The Global Sustainability Network ( GSN ) is pursuing the United Nations Sustainable Development Goal number 8 with a special emphasis on Goal 8.7 which ‘takes immediate and effective measures to eradicate forced labour, end modern slavery and human trafficking and secure the prohibition and elimination of the worst forms of child labour, including recruitment and use of child soldiers, and by 2025 end child labour in all its forms’.
The origins of the GSN come from the endeavours of the Joint Declaration of Religious Leaders signed on 2 December 2014. Religious leaders of various faiths, gathered to work together “to defend the dignity and freedom of the human being against the extreme forms of the globalisation of indifference, such us exploitation, forced labour, prostitution, human trafficking” and so forth.
tinyurlis.gdv.gdv.htu.nuclck.ruulvis.netshrtco.detny.im
